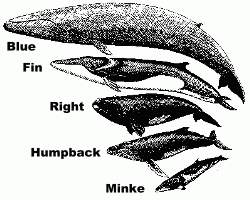
|
Balaenoptera musculus Blue whales are the largest animals to have ever existed .... larger even than the biggest dinosaur. Some have been as long as 33 metres (110 feet), but most are in the 24-27 metre range. Blue whales can weigh up to 110 tonnes (120 tons). They have a life expectancy of 35-40 years. Blue whales are bluish-grey in colour, and their underside is slightly lighter. 
  Blue whales are baleen whales, which means that they eat tiny organisms that they filter out of the water, using huge comb-like baleen plates in the back of their throat. The throat skin has many grooves which expand as the whale gulps water into its mouth. After water and food has been sucked in, the whale pushes the water back out through the baleen plates, which may be a metre in length - the longest of any baleen whale.
Blue whales are baleen whales, which means that they eat tiny organisms that they filter out of the water, using huge comb-like baleen plates in the back of their throat. The throat skin has many grooves which expand as the whale gulps water into its mouth. After water and food has been sucked in, the whale pushes the water back out through the baleen plates, which may be a metre in length - the longest of any baleen whale.Blue whales feed on tiny organisms called krill. Krill are tiny shrimp that live in large schools in almost every ocean of the world. They are one of the most plentiful food species (except for insects) on earth. The baleen in the whale's throat filters out krill by the thousands. Small fish and plankton are also caught by the baleen. It may take as much as 3500 kg of krill and small fish a day to keep the Blue whale healthy. 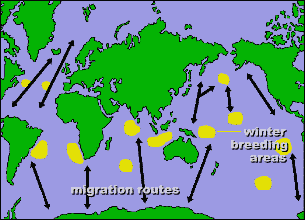 Blue whales live in almost every ocean, although their numbers are limited. Hunting drove them nearly to extinction, and their numbers are still low, especially in the North Atlantic Ocean. Most live in the southern hemisphere, but can also be seen off the coast of California, in the Gulf of California in Mexico, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence in Canada, and also northern regions of the Indian Ocean. Blue whales live in almost every ocean, although their numbers are limited. Hunting drove them nearly to extinction, and their numbers are still low, especially in the North Atlantic Ocean. Most live in the southern hemisphere, but can also be seen off the coast of California, in the Gulf of California in Mexico, in the Gulf of St. Lawrence in Canada, and also northern regions of the Indian Ocean.Blue whales are fast swimmers, able to reach speeds of 30 km/h if chased. Whales are mammals, and must surface to breathe, but they can hold their breath a long time ... dives can last anywhere up to 20 minutes. Blue whales also make very loud sounds. The low-frequency sounds they make when they communicate with each other have been recorded as loud as 188 decibels, and can be heard as far as 800 km away. (For comparison, a commercial jet taking off makes a sound of 120 db). Learn more about sound, and hear a blue whale here. The buoyant force of water in the whale's ocean environment is one reason that it can grow so large. Instead of relying on just a skeleton to support its weight, the buoyancy of the surrounding ocean water supports the whale's body tissues. If a Blue whale were to be removed from the ocean, it would be crushed to death by its own weight.  Packs of Killer whales have been known to attack and kill young Blue whales, but the Blue whale's main predator has been man. Blue whales were hunted nearly to extinction, until the International Whaling Commission declared them to be a protected species in 1966, because of the huge decrease in their population. Blue whales comprised about 90 percent of the whaling industry’s total catch during the early part of the twentieth century; in 1931, more than 30,000 were killed, for their blubber, flesh, bones, and body oils . Today it is believed that about 11,000 still exist.
Blue whale jawbone |