Burning Hydrocarbons
Let's look at what happens when methane burns. First, the gas is mixed in with molecules of oxygen from the air. A spark is necessary to begin the reaction.
Once the reaction begins, it is self-sustaining, since it's exothermic.
|

|

|
All the molecules of methane are ripped apart. So are the molecules of oxygen. The hydrogen atoms, carbon atoms, and oxygen atoms are free, and able to recombine.
|
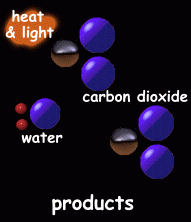
The hydrogen atoms combine, in pairs, with oxygen atoms, to make molecules of water (H2O).
Carbon atoms combine with pairs of oxygen atoms to make carbon dioxide molecules (CO2).
Heat and light are also given off.
|
|
The simple (unbalanced) equation that describes this reaction is:
methane + oxygen ----> water + carbon dioxide + energy
CH4 + O2 ----> H2O + CO2 + energy
The balanced equation:
CH4 + 2·O2 ----> 2·H2O + CO2 + energy
Back
|