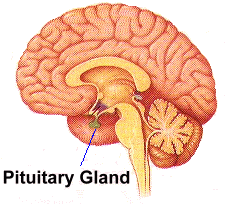
The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain. It is sometimes called the 'master gland' because its hormones affect many of the body's organs.
The pituitary gland is divided into two parts, front (anterior) and back (posterior).
The anterior pituitary produces several hormones:
- Prolactin or PRL: stimulates milk production from a woman's breasts after childbirth. It also affects sex hormone levels in both men and women.
- Growth hormone or GH: this hormone promotes growth in children; in adults it is used by the body to maintain muscle and bone mass. It can also affect how fat is distributed in the body.
- Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH: controls production of cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cortisol helps maintain blood pressure and blood glucose levels.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH: controls the production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid, which regulate the body's metabolism, growth and development, and nervous system.
- Luteinizing hormone or LH: this hormone controls testosterone levels in men and estrogen levels in women.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH: this causes sperm production in men and makes the ovaries release eggs in women. LH and FSH working in combination control the normal functioning of the ovaries or testes.
The posterior pituitary produces two hormones:
- Oxytocin: this hormone causes milk production in nursing mothers, and contractions during childbirth.
- Antidiuretic hormone or ADH: Also called vasopressin, this hormone regulates the body's water balance. If this hormone malfunctions, it can lead to problems with sodium build-up, and adversely affect the kidneys.
Because the pituitary gland's hormones control the release of other hormones by other glands and organs, a problem with the pituitary gland (in particular, how much or how little of its hormones that get released) can lead to many other problems in the body.
BACK
|