  Integers are positive or negative whole numbers.
Integers are positive or negative whole numbers.Positive integers can be written with a positive sign: +7 or without the sign: 7 Negative integers are written with a negative sign: -11 The number zero is neither positive nor negative. The magnitude of an integer is how far it is from zero on a number line. 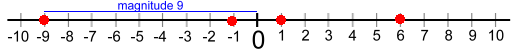
On the number line above: The magnitude of -9 is 9 units. The magnitude of +6 or 6 is 6 units. The magnitude of -1 is 1 units. The magnitude of 1 is 1 unit. Every positive number has an opposite negative number with the same magnitude. 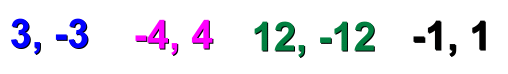
A number and its opposite are called additive inverses. For example, the additive inverse of 5 is -5 
Positive integers are always greater than negative ones: 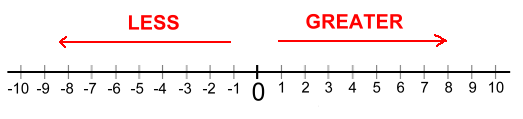
3 is greater than -11 3 > -11 The bigger a negative number's magnitude, the smaller it is! -9 is less than -2 -9 < -2 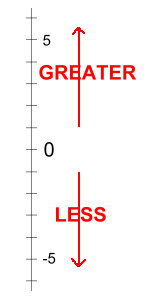 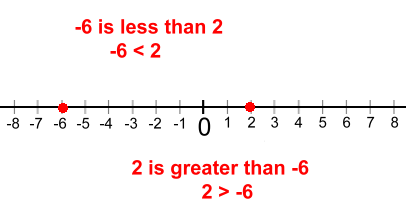 Let's move on to page two, where we'll look at some real examples of integers in use, and let you try some practice questions ... |