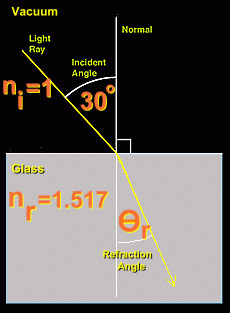
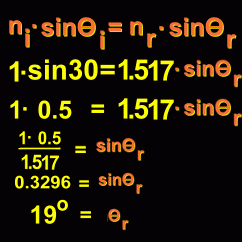  Refraction is what happens when light passes from one translucent medium to another. As light enters a new medium, its speed changes, and its direction of travel changes. It is this change in direction, or 'bending' of light, that is commonly referred to as refraction. You are familiar with this phenomenon where light changes direction. It is what causes a spoon in a glass of water to appear bent. It makes things in the distance on a hot day appear to 'waver' as hot air rises from the ground and light passing through it changes its direction. It makes above-water spear fishing difficult because the fish below the surface aren't where they appear to be. And it makes sunset last a few seconds longer as light from the already set sun refracts around the earth through the atmosphere. 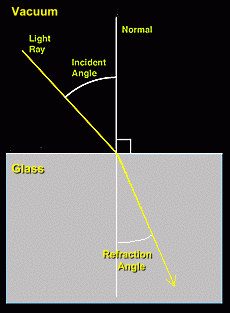 Let's look more closely at what happens when a ray of light passes from one medium into another. For example, suppose a light beam goes from vacuum down into a piece of glass. Let's look more closely at what happens when a ray of light passes from one medium into another. For example, suppose a light beam goes from vacuum down into a piece of glass. Notice the perpendicular line that marks the spot where the light enters the glass; this is called the normal line. The top part of the diagram (the vacuum), where the light originates, is called the incident side; the bottom (glass), the new medium that the light enters, is called the refracted side. The angles that the beam of light makes with the normal line on each side are marked and labelled on the diagram. Notice that they are not the same. In fact, light behaves in a very predictable way when it enters a new medium. In general, when entering a denser medium, light will refract (bend) towards the normal. Similarly, when light leaves a dense medium and enters a less dense one, it bends away from the normal. The amount of bending, or angle of refraction, can be calculated using a formula. Every translucent substance has a number associated with it that is a measure of how much light will bend in that substance. This number is called the index of refraction, and has the symbol n. The larger the value of 'n', the more that light will bend in that substance, if coming from a vacuum. Here are some indicies of refraction for various substances. You will notice that denser substances tend to have higher values of 'n':
The math involved isn't very difficult, although you have to know about trigonometric functions like sine. Now you understand what happens when a beam of light passes from one medium to another. |