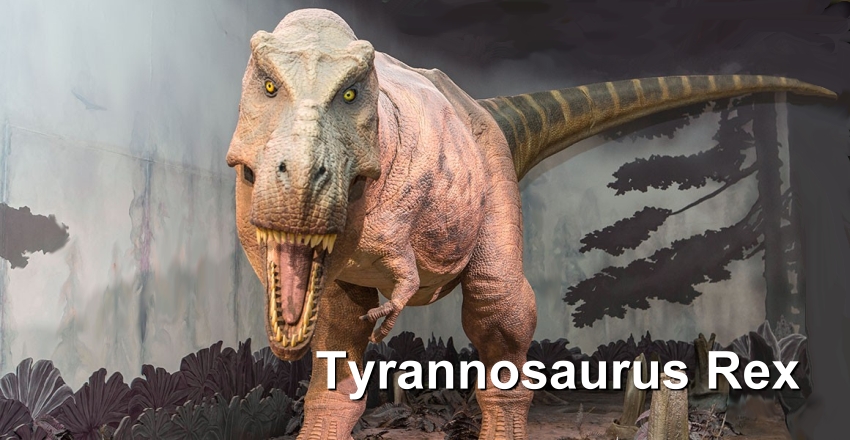
 Tyrannosaurus Rex, or T. rex, was a large theropod, the largest of the tyrannosaurs, that lived during the Upper Cretaceous period, 68 to 66 million years ago. 'Tyrannosaurus' is Greek for 'tyrant lizard,' and 'rex' means 'king' in Latin. So, Tyrannosaurus rex was 'King of the Tyrant Lizards.' T. rex could grow to lengths of over 12.5 m and weigh 9 metric tonnes. It was among the largest known land predators, and is estimated to have exerted the strongest bite force among all terrestrial animals. This allowed it to crush bones while biting, and completely consume the carcasses of large dinosaurs As the largest carnivore in its environment, Tyrannosaurus rex was an apex predator, preying upon hadrosaurs and young armoured herbivores like ceratopsians and ankylosaurs, and perhaps sauropods ('long-necks'). It lived throughout what is now western North America T. rex had senses similar to those of its close relatives, birds and crocodiles. Because of its forward-facing eyes, it may have had better depth perception than most other predatory dinosaurs. Most paleontologists today accept that Tyrannosaurus was both an active predator and a scavenger. T. rex hatchlings were gangly, and turkey-sized.  T. rex grew much faster than reptiles do today; scientists think that it reached its full size in less than 20 years. Based on growth rings in fossil bones, scientists know that the longest-lived T. rex specimen ever found was 28 when it died, and had suffered many injuries over its lifetime, including at least one bite from another T. rex.
T. rex grew much faster than reptiles do today; scientists think that it reached its full size in less than 20 years. Based on growth rings in fossil bones, scientists know that the longest-lived T. rex specimen ever found was 28 when it died, and had suffered many injuries over its lifetime, including at least one bite from another T. rex.T. rex's olfactory bulbs, the part of the brain used to process smell, were large, and scientists believe that T. rex had a good sense of smell, much like other predatory dinosaurs. Its arms were powerfully muscled, ending in two mobile fingers with large claws. Scientists aren't sure how T. rex used its arms, but they know that they were far too short to help with eating. The abundance of fossil material compared to most other dinosaurs has resulted in significant research into many aspects of the T. rex's biology. Specimens of Tyrannosaurus rex include some that are nearly complete skeletons. Soft tissue and proteins have been reported in at least one of these specimens. Some of the best tyrannosaur skeletons that have been found have come from the rich badlands of western Canada, which was home to a diverse group of tyrannosaurs, including the earlier Albertosaurus, and of course T. rex. The climate was warmer than it is now; lush plant life supported a diverse animal community ranging from dinosaurs to mammals to insects.  T. rex was illustrated many decades ago as walking upright. Since then, research has suggested that its bone structure wouldn't have supported this. Now representations in museums, art, and film show T. rex with its body approximately parallel to the ground with the tail extended behind the body to balance the head. Recent computer models and other evidence also suggest that T. rex did not run, but walked at speeds up to 24 km/h.
T. rex was illustrated many decades ago as walking upright. Since then, research has suggested that its bone structure wouldn't have supported this. Now representations in museums, art, and film show T. rex with its body approximately parallel to the ground with the tail extended behind the body to balance the head. Recent computer models and other evidence also suggest that T. rex did not run, but walked at speeds up to 24 km/h.
There is some fossil evidence to support the idea that T. rex may have had feathers like many other smaller dinosaurs, but that they were likely confined to small patches on the head and tail. T. rex was certainly the biggest two-legged predator in the late Cretaceous ecosystem, and it was one of the largest predators ever to live on land. Other species, such as Carcharodontosaurus, Giganotosaurus and Spinosaurus, were similar in size but lived earlier in the Cretaceous Period. They belonged to different families of predatory dinosaurs than T. rex. 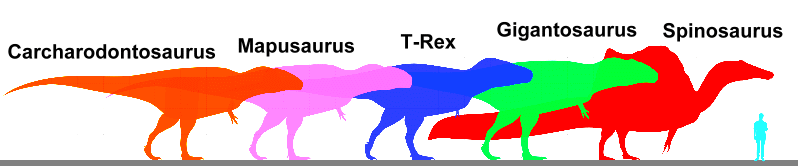 |