 A nuclear reaction at the Sun's core creates massive amounts of radiation, or energy. This energy, also known as the electromagnetic spectrum, includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. 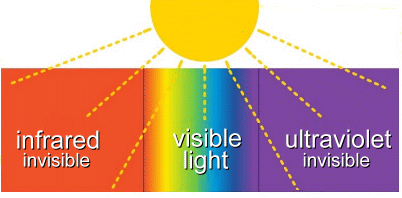 Depending on its wavelength, different types of solar radiation do different things:
  
Ultraviolet (UV) light has shorter wavelengths than visible light. Although UV waves are invisible to the human eye, some insects, such as bumblebees, can see them. UV light also has a higher frequency than visible light, which means it carries more energy. There are three types of UV radiation: 
Almost all skin cancers are caused by over-exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the Sun and tanning beds. The earth's ozone layer protects us from most of the sun's harmful UV rays. But over time, the release of certain chemicals into the environment has damaged the ozone layer. As the ozone layer thins, more UV reaches the earth's surface. Many countries around the world, including Canada, have recognized this problem and have taken steps to protect the ozone layer from more damage. Efforts have focused mainly on controlling the production and use of chemicals known to damage the ozone layer. These chemicals are used mainly in refrigeration and air-conditioning. Fortunately, bans on the production and use of these chemicals have resulted in considerable healing of the ozone layer. The UV Index is a numerical scale developed by the World Health Organization. The UV index measures the amount of UV radiation reaching the earth’s surface. It begins at zero and has no upper limit; the rating usually finishes at 11+, which is extreme. Astronomical Research Since the Earth's atmosphere absorbs much of the high-energy ultraviolet radiation, scientists use data from satellites positioned above the atmosphere, in orbit around the Earth, to sense UV radiation coming from our Sun and other astronomical objects. Scientists can study the formation of stars in ultraviolet, since young stars shine most of their light at these wavelengths. |