|
What happens to the water after it rains? Where does it go? How does the water get into the sky in the first place? If you don't know the answers to these questions, then this page is for you! The heat from the sun causes water in lakes, rivers, and the ocean, to evaporate. This means that it turns from a liquid to a gas, and 'disappears' into the air. The water in the lakes and rivers, and even the ocean, is constantly evaporating into the air. Does this mean that all our lakes and rivers, and even the ocean, will eventually disappear? Fortunately, no. When water vapour cools off in the air, it turns back into water droplets. This is called condensation. You can watch invisible water vapour turn back into liquid water droplets yourself. Just take a cold glass and fill it with an icy drink, on a warm day. Water vapour in the air will hit the glass and cool off, turning back into liquid water ... which you will see as drops on the side of the glass. It is condensation which makes the water vapour in the air come back to the lakes, rivers, and oceans ... as rain! Here's how it works. The hot sun helps water in the lakes and oceans to evaporate. This turns the liquid water into a gas called water vapour, which goes up into the air. This water vapour in the air will cool off when it rises up into the sky, and turn back into water droplets. When enough of these water droplets have condensed in the air, we can see the water as a cloud (which is really just a mist of many water droplets). The cloud may be blown by the wind. Sooner or later it will rise again, and the air around it will be even cooler. After a while, the cool air can't hold the water droplets up any more, and they fall to the ground as rain. Eventually the rainwater will seep through the layers of the ground and back into the lakes and oceans again! It's called the water cycle because it happens over and over. Here's a picture that will make it clearer. 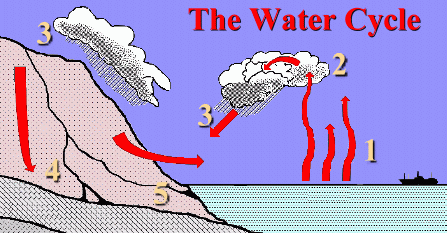
|