 Ecology is the study of the homes of animals and plants. Ecologists are interested in where animals and plants live, and how they interact with each other.
The 'Food Web' of living creatures can be divided into three groups:
Ecology is the study of the homes of animals and plants. Ecologists are interested in where animals and plants live, and how they interact with each other.
The 'Food Web' of living creatures can be divided into three groups:
- Producers are organisms which produce their own food through photosynthesis
- Consumers are organisms which don't make their food, but get it from eating plants or animals
- Decomposers are organisms which digest or break down living material which has died
More About Decomposers:
Bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes are the three most common types of decomposers in the environment. They break down dead organisms into nutrients, (we call this process 'rotting'), and these nutrients are then returned to the soil. If it weren't for decomposers, we'd be up to our armpits in dead things!
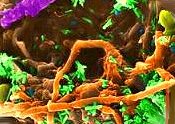 Bacteria are the smallest living organisms, and the most numerous of decomposers; they make up 90% of the billions of microorganisms typically found in a gram of soil. Bacteria can thrive in any environment; they can be found in the cold Antarctic wilderness, in the intense heat of a steamy geyser, or in the acidic contents of your stomach. They will eat things as diverse as a dead animal carcass to an oil slick on the surface of the ocean, and often produce methane as a byproduct. Bacteria are the smallest living organisms, and the most numerous of decomposers; they make up 90% of the billions of microorganisms typically found in a gram of soil. Bacteria can thrive in any environment; they can be found in the cold Antarctic wilderness, in the intense heat of a steamy geyser, or in the acidic contents of your stomach. They will eat things as diverse as a dead animal carcass to an oil slick on the surface of the ocean, and often produce methane as a byproduct.
 Fungi is the name for simple organisms including molds and yeasts. Next to bacteria, fungi are the most efficient decomposer organisms. Molds can grow both as unseen filaments, or as gray, blue, or white fuzzy colonies on the surface. Fungi are important because they break down tough organisms like wood, enabling bacteria to continue the decomposition process once most of the cellulose has been exhausted. Fungi are important in the composting process. The picture on the right shows a fungus helping to rot a stump of a tree. Fungi is the name for simple organisms including molds and yeasts. Next to bacteria, fungi are the most efficient decomposer organisms. Molds can grow both as unseen filaments, or as gray, blue, or white fuzzy colonies on the surface. Fungi are important because they break down tough organisms like wood, enabling bacteria to continue the decomposition process once most of the cellulose has been exhausted. Fungi are important in the composting process. The picture on the right shows a fungus helping to rot a stump of a tree.
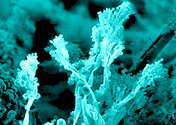 Molds are also common decomposers, and are responsible for much of the rotting which takes place in food. Molds grow long filaments, and reproduce using spores. Shown at the left is a simple bread mold.
Fungi live on leaves and wood in your compost pile. Many fungi can break down the cellulose in leaves. They can also degrade wood, which is made of large, complex molecules called lignins. Wood also contains the long tough molecules of cellulose, the stuff that paper is made from. Fungi are the most efficient organisms at breaking down wood. Molds are also common decomposers, and are responsible for much of the rotting which takes place in food. Molds grow long filaments, and reproduce using spores. Shown at the left is a simple bread mold.
Fungi live on leaves and wood in your compost pile. Many fungi can break down the cellulose in leaves. They can also degrade wood, which is made of large, complex molecules called lignins. Wood also contains the long tough molecules of cellulose, the stuff that paper is made from. Fungi are the most efficient organisms at breaking down wood.
Actinomycetes are a form of fungi-like bacteria that form long filaments that stretch through the soil. Actinomycetes are the primary decomposers of tough plant tissues like bark, paper and stems. Soilís "earthy" smell is caused by actinomycetes at work.
They are especially effective at softening up tough materials, such as cellulose, chitin, and lignin.
Larger decomposers include maggots and other creatures.
Main Page
|