 Differentiation in mathematics is the process you use to find the rate at which a quantity changes with respect to something else. The rules for differentiating algebraic functions or combinations of functions are described below, along with an example of each. Following standard practice, we'll use c as a constant, n as any Real number, u and v as functions of x, and y as a function of u. The Constant Rule 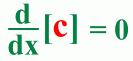
Here's an example: The Constant Multiple Rule 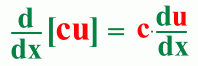
Here's an example: 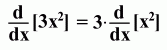
The Sum Rule 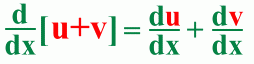
Here's an example: 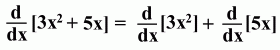
The Difference Rule 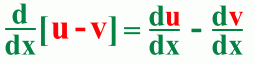
Here's an example: 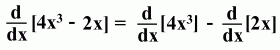
The Product Rule 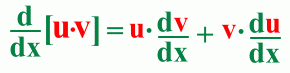
Here's an example: The Quotient Rule 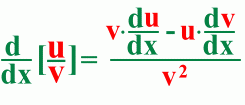
Here's an example: 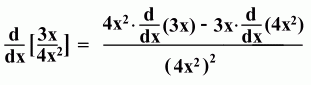
The Power Rule 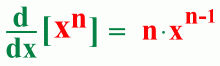
Here's an example: The Chain Rule 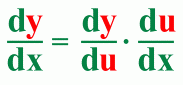
Here's an example: 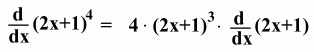
You probably noticed that we didn't finish simplifying some of our examples above. If you'd like to see some examples that are completely finished, go on to page two. |