 Infrared light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. People encounter infrared waves every day; the human eye can't see them, but we can feel them as heat. 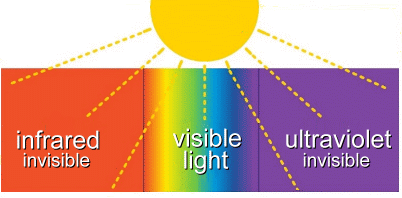 In 1800, William Herschel conducted an experiment measuring the difference in temperature between the colours in the visible spectrum. He placed thermometers within each colour of the visible spectrum. The results showed an increase in temperature from blue to red. When he noticed an even warmer temperature measurement just beyond the red end of the visible spectrum, Herschel realized he had discovered infrared light. 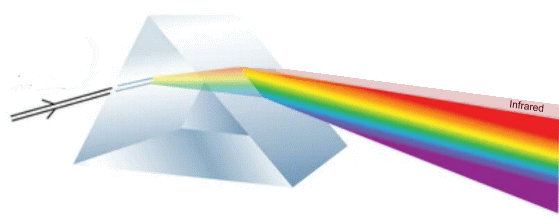  We can sense some infrared energy as heat. Some objects are so hot they also emit visible light, such as a fire does. Other objects, like humans, are not as hot, and only emit infrared waves. Our eyes can't see these infrared waves, but instruments that can sense infrared energy, such as night-vision goggles or infrared cameras, allow us to 'see' the infrared waves being emitted from warm objects such as humans or animals.
We can sense some infrared energy as heat. Some objects are so hot they also emit visible light, such as a fire does. Other objects, like humans, are not as hot, and only emit infrared waves. Our eyes can't see these infrared waves, but instruments that can sense infrared energy, such as night-vision goggles or infrared cameras, allow us to 'see' the infrared waves being emitted from warm objects such as humans or animals.
A remote control uses infrared light waves to change channels on your TV. Heat lamps and stovetop elements often emit both visible and infrared energy.  Many objects in the universe are too cool and faint to be detected in visible light, but can be detected by their infrared emissions. The Cassini spacecraft captured this image of Saturn's aurora using infrared waves. The false-colour images show Saturn's aurora glowing in green around the planet's south pole. Charged particles streaming in from the Sun are experiencing some type of magnetism above Saturn that was previously unexpected.
Many objects in the universe are too cool and faint to be detected in visible light, but can be detected by their infrared emissions. The Cassini spacecraft captured this image of Saturn's aurora using infrared waves. The false-colour images show Saturn's aurora glowing in green around the planet's south pole. Charged particles streaming in from the Sun are experiencing some type of magnetism above Saturn that was previously unexpected.
Infrared waves have longer wavelengths than visible light and can pass through dense regions of gas and dust in space with less scattering and absorption. Iinfrared light can reveal objects that can't be seen in visible light using optical telescopes. The James Webb Space Telescope has three infrared instruments to help study the origins of the universe and the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets. As solar radiation hits Earth, some of this energy is absorbed by the atmosphere and the surface, causing a warming of the planet. This heat is then emitted from Earth in the form of infrared radiation. Instruments onboard Earth-observing satellites can sense this emitted infrared radiation and use the resulting measurements to study changes in land and sea surface temperatures. 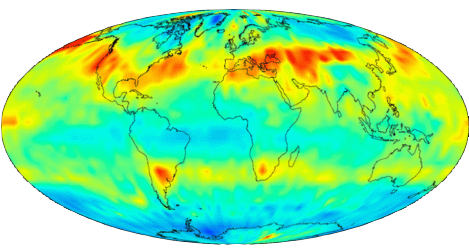 |