
Page Three
|
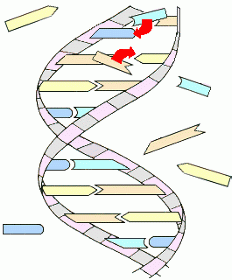
In order for DNA to duplicate itself, the surrounding cell fluid must contain all of the raw materials ... nucleotides (all four kinds), sugars, phosphates, and special enzymes. One of these enzymes is called DNA polymerase, and its function is to 'unzip' the two strands of the DNA molecule.

As the two strands of DNA ladder come apart, each contains the complete original pattern (although one is a 'mirror image' of the other). Each newly exposed nucleotide 'rung' now attracts and bonds to a corresponding new nucleotide from the cell fluid.
Gradually each half of the DNA molecule gets its opposite half rebuilt from surrounding raw materials. As the DNA unzips, two new DNA molecules form from the halves, and each is an exact copy of the original!
|
The process of duplication is exact. This is remarkable when you consider how long a DNA molecule is. If all the pieces of DNA in just one human cell were joined end to end, the resulting strand would be a metre long and would contain about 6 million pairs of nucleotides. Every time a DNA molecule reproduces, all 6 million pairs of nucleotides separate and then rebuild the full molecule.
This model of the DNA molecule was first described by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. They figured out what was happening without benefit of any actual pictures of the molecule, which was too small to see.
Page One | Page Two | Page Three | Main Page
|


