 The Fibonacci Sequence is the series of numbers: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ... Each number is found by adding the two numbers before it: 1 = 1 = 2 1 + 2 = 3 2 + 3 = 5 etc ... The next number above would be 21 + 34 = 55 Here is a longer list: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181, 6765, 10946, 17711, 28657, 46368, 75025, 121393, 196418, 317811, ... The rule describing how to find terms in the sequence is a recursive formula: tn = tn-1 + tn-2 where: tn is term number "n" tn-1 is the previous term (n-1) tn-2 is the term before that (n-2) For eaxample: t11 = t10 + t9 The Golden Ratio The Greek Pythagoras, who lived in the 5th century B.C. and is best known for discovering the theorem about right triangles that bears his name, has also been credited with discovering the golden ratio. It's also called the golden mean or the golden section. The golden ratio is usually rounded off to 1.618 (the number is actually irrational, like π). The golden ratio is represented by φ (phi), the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. The golden ratio of 1.618 has been important to mathematicians, scientists, and artists for centuries. It is derived from the Fibonacci sequence. The quotient between each successive pair of Fibonacci numbers in the sequence approximates 1.618, closer and closer as the terms increase in size.  The golden ratio appears in the arts. Rectangles and shapes within rectangles with a length to width ratio of about 1.6 are considered esthetically pleasing, and were often incorporated into works of art and architecture. For example, consider the Great Pyramid in Giza.
The golden ratio appears in the arts. Rectangles and shapes within rectangles with a length to width ratio of about 1.6 are considered esthetically pleasing, and were often incorporated into works of art and architecture. For example, consider the Great Pyramid in Giza. By taking the slant height of this pyramid and dividing by half the base length you get 1.61804.  Many things in nature also have properties that exhibit the ratio 1.618. For example, in every bee hive there is one female queen bee who lays all the eggs. If an egg is not fertilised it eventually hatches into a male bee, called a drone. If an egg is fertilised by a male bee, then the egg produces a female worker bee, who doesn't lay any eggs herself. In theory, all male honeybees only have one parent, while female honeybees have two. The number of ancestors in past generations of any particular bee, ignoring sibling ancestors, would follow the Fibonacci sequence.
Many things in nature also have properties that exhibit the ratio 1.618. For example, in every bee hive there is one female queen bee who lays all the eggs. If an egg is not fertilised it eventually hatches into a male bee, called a drone. If an egg is fertilised by a male bee, then the egg produces a female worker bee, who doesn't lay any eggs herself. In theory, all male honeybees only have one parent, while female honeybees have two. The number of ancestors in past generations of any particular bee, ignoring sibling ancestors, would follow the Fibonacci sequence. The result is that if you divide the number of female bees by the number of male bees in any given hive, you will get a number near 1.618. 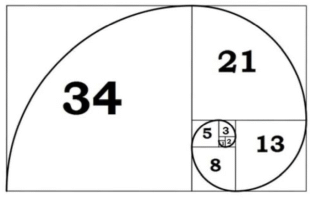 The limits of the squares of successive Fibonacci numbers create a spiral known as the Fibonacci spiral. It follows turns by a constant angle close to the golden ratio and is commonly called the golden spiral. The numbers of spirals in pinecones, for example, are Fibonacci numbers, as is the number of petals in each layer of most flowers. In spiral-shaped plants, each leaf grows at an angle compared to its predecessor, and sunflower seeds are packed in a spiral formation in the center of their flower in a geometry governed by the golden ratio.
The limits of the squares of successive Fibonacci numbers create a spiral known as the Fibonacci spiral. It follows turns by a constant angle close to the golden ratio and is commonly called the golden spiral. The numbers of spirals in pinecones, for example, are Fibonacci numbers, as is the number of petals in each layer of most flowers. In spiral-shaped plants, each leaf grows at an angle compared to its predecessor, and sunflower seeds are packed in a spiral formation in the center of their flower in a geometry governed by the golden ratio.
 |