 Page Three 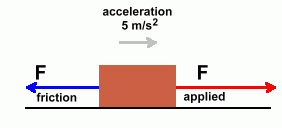 Let's look at a real problem. We'll use our 20 kg mass again, with a coefficient of friction of 0.4, and apply a force to it that causes it to accelerate at 5 m/s2.
Let's look at a real problem. We'll use our 20 kg mass again, with a coefficient of friction of 0.4, and apply a force to it that causes it to accelerate at 5 m/s2.
The question is this: "What force must you apply to cause this acceleration?" This is not a trivial problem, since friction is involved. Some of your applied force must be used to overcome that friction. Step 1: Calculate the net force 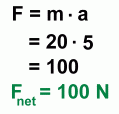 The acceleration of 5 m/s2 is the result of whatever force is left over after friction is subtracted. So if we use that acceleration to calculate a force, it will be the net force. The acceleration of 5 m/s2 is the result of whatever force is left over after friction is subtracted. So if we use that acceleration to calculate a force, it will be the net force.The result is shown on the left. The net force that resulted in an acceleration of 5 m/s2 must have been 100 N. Step 2: Calculate the frictional force 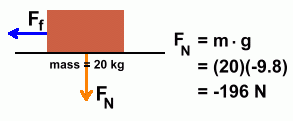 We'll need to work out the normal force first.
We'll need to work out the normal force first.We've already done this for our 20 kg mass, but here's the calculation again. We'll ignore the negative sign. The normal force is 196 N. The frictional force is given by the equation So the friction force works out to be: Ff = 0.4 · 196 = 78.4 N Step 3: Calculate the applied force 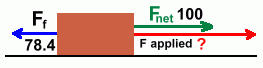 Here's what we have so far.
Here's what we have so far.The net force is only 100 N. It's what's left, after overcoming a 78.4 N frictional force. How much was the force that was applied? This is clearly just an addition problem. The original force applied must have been 178.4 N. Now let's look at forces applied to an object at an angle. Go on to page four. |