 There are about 600 muscles in the human body. The brain, the nervous system and the skeletal muscles work together to cause movement – this is collectively known as the neuromuscular system. Muscles perform a lot of functions in the body, from pumping blood and helping the body to move, to lifting, digesting food or giving birth. Muscles work by either contracting or relaxing to cause movement. This movement may be voluntary (meaning the movement is made consciously) or involuntary (done without our conscious awareness). Glucose from carbohydrates in what we eat fuels our muscles. Muscle tissue also needs minerals, electrolytes and other substances such as calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium. The three main types of muscles include skeletal, smooth and cardiac. 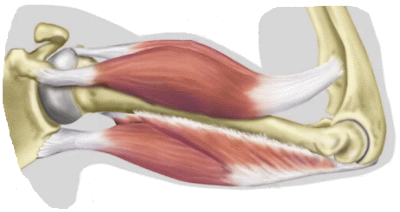 Skeletal muscles
Skeletal musclesThis is tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. Skeletal muscle is grouped into opposing pairs, such as the biceps and triceps on the front and back of the upper arm. Skeletal muscles are under conscious control; they are known as voluntary muscles. Generally speaking, skeletal muscles come in four main shapes, including:
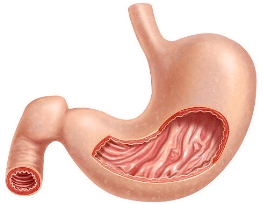 Smooth muscles
Smooth muscles These are located in various internal structures, including the stomach, uterus and blood vessels. Smooth muscle is arranged in layered sheets that contract in waves along the length of the structure. These are involuntary muscles, since their motion happens without our conscious awareness. 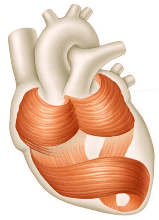 Cardiac muscle
Cardiac muscle This muscle is specific to the heart. The heart contracts and relaxes without our conscious awareness, so these also are involuntary muscles. Cardiac muscle tissue forms the bulk of the heart. Contracting heart muscle uses a lot of energy, so it requires a constant flow of blood to provide oxygen and nutrients. Blood is brought to the muscle by the coronary arteries. These lie on the outer surface of the heart. Blood is then drained away by the coronary veins. |