  Salt is a natural mineral composed of two elements: sodium and chlorine. Pure salt is about 40% sodium and 60% chloriine by weight.
Salt is a natural mineral composed of two elements: sodium and chlorine. Pure salt is about 40% sodium and 60% chloriine by weight.
In chemistry, a salt is substance produced by the reaction of an When in solution, most salts are good conductors of electricity.  Sodium is a soft silvery-white metal, a chemical element with symbol Na and atomic number 11. It tarnishes within seconds of being exposed to the air, and is highly reactive when added to water, sometimes igniting spontaneously. It is never found free in nature, but in compound form is the fourth most abundant element on earth.
Sodium is a soft silvery-white metal, a chemical element with symbol Na and atomic number 11. It tarnishes within seconds of being exposed to the air, and is highly reactive when added to water, sometimes igniting spontaneously. It is never found free in nature, but in compound form is the fourth most abundant element on earth.Sodium is used as a heat exchanger in some nuclear reactors. It is a component of both baking soda (NaHCO3) and borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O), as well as table salt (NaCl).  Chlorine is a non-metal element on the periodic table with the chemical symbol Cl and atomic weight 17. It is normally a yellowish-green gas that is toxic, corrosive, and irritating to the eyes and the respiratory system.
Chlorine is a non-metal element on the periodic table with the chemical symbol Cl and atomic weight 17. It is normally a yellowish-green gas that is toxic, corrosive, and irritating to the eyes and the respiratory system.Pure chlorine can be found in trace amounts in volcanic gases, but is mostly found in compounds with other elements. It is a component of the acid naturally produced inside our stomach, One fascinating thing about how chemistry works is that very different elements can combine to produce a compound that is unlike either. In this case, the highly reactive metal sodium combines with the toxic and corrosive gas chlorine to produce the stable and safely edible compound table salt! 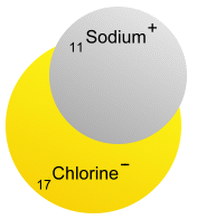
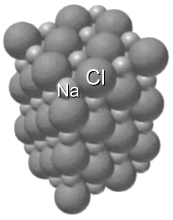 The molecular formula of table salt, sodium chloride, is NaCl, and the compound exists as a mineral, often mined from deep within the earth. Table salt is an ionic compound. Sodium Na+ and chlorine Cl- ions are present in equal numbers, arranged to form a cubic crystal lattice. Salt is obtained two different ways. It can be mined from huge beds of sedimentary minerals that result from the drying up of ancient lakes and seas. It can also be produced by evaporating seawater.  A salt mine Salt is an important ingredient in cooking. But salt doesn't only add flavour to meals. It has played an important role in preserving food, since bacteria can't live in a high-salt environment. Salting foods such as meat and fish to preserve them draws water out, removing water as a source of nutrients for microbes, keeping the foods fresher longer. Your body needs some salt, but too much can be bad for you. Too much sodium in the diet can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Conversely, not getting enough salt in your diet has been linked to low blood pressure, thyroid problems, and dehydration. Salt is also necessary to maintain the right fluid balance in the body. For your thyroid to work properly, your body needs the mineral iodine; iodine deficiency prevents your body from producing enough of the thyroid hormone. Symptoms of a deficiency include an enlarged thyroid, constipation, difficulty thinking, fatigue, and sensitivity to cold. As a result, iodine is added to many salts (they are labeled "iodized"). According to the American Heart Association, you should keep sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams (mg) per day, which you can get from a little less than a tablespoon of table salt. And no more than 1,500 mg a day is ideal for most adults. This can be very difficult to do, as salt is added to almost all processed foods. |