 Lice, along with the scabies mite, are the most common parasites that infect humans. These are transmitted by personal contact, including sexual contact. An infestation of pubic lice (Phthirus pubis, or the crab louse) is most common in adolescents and young adults. Pubic lice will be found in the hair-bearing areas of the body, especially the groin. Lice can also be spread from person to person through contact with clothing and contaminated items such as towels.  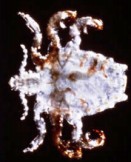 A louse gets onto the skin of a person and lays eggs. After a week or so the eggs hatch, releasing baby lice that grow into adults and multiply again (usually within 15 days). Both baby and adult lice feed on human blood. The most obvious symptom that you have been infected with lice or pubic lice (crabs) is an intense itchiness at the infected area. Often the itchiness is worse at night. There may be small red or bluish irritations on the skin. Crab eggs (nits) attach to the hairs of your body, appearing to the naked eye as tiny white-grey specks. Sometimes the crab louse can even be seen moving within the pubic hair. The only sure way to avoid getting lice is to avoid people who already have them. Protection during sex will not prevent the spread of lice, as even close contact, intimate or otherwise, can spread the infection. Lice can be killed with an appropriate anti-parasite medication, although retreatment may be necessary. It is also important to decontaminate all clothing and bedding by machine-washing in hot water. . GONORRHEA | GENITAL WARTS | LICE & CRABS | SCABIES | HEPATITIS | HIV/AIDS |